LED (Light Emitting Diode) headlamp bulbs have gained popularity in recent years due to their energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and improved visibility compared to traditional halogen bulbs. However, LED bulbs generate a significant amount of heat during operation, which can lead to performance issues and even failure if not properly managed. This is where active cooling comes into play. In this article, we'll explore the reasons why LED headlamp bulbs require active cooling and how it benefits their performance and longevity.
1. Heat generation in LED bulbs
While LED bulbs are more energy-efficient than halogen bulbs, they still generate heat during operation. The heat is primarily produced by the LED chip itself and the electronic components that regulate the power supply to the LEDs. If this heat is not dissipated effectively, it can cause the LED chip to overheat, leading to reduced light output, color shifting, and even premature failure.
2. Compact design limitations
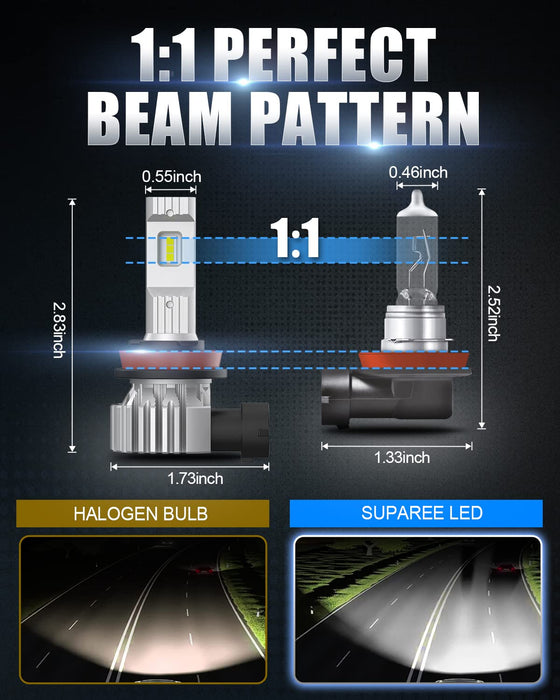
LED headlamp bulbs are designed to fit into the same space as traditional halogen bulbs, which limits the amount of space available for heat dissipation. Unlike halogen bulbs, which dissipate heat through the bulb's glass surface, LED bulbs rely on a heatsink to draw heat away from the LED chip. However, the compact design of LED bulbs makes it challenging to incorporate a large enough heatsink to dissipate the heat effectively.
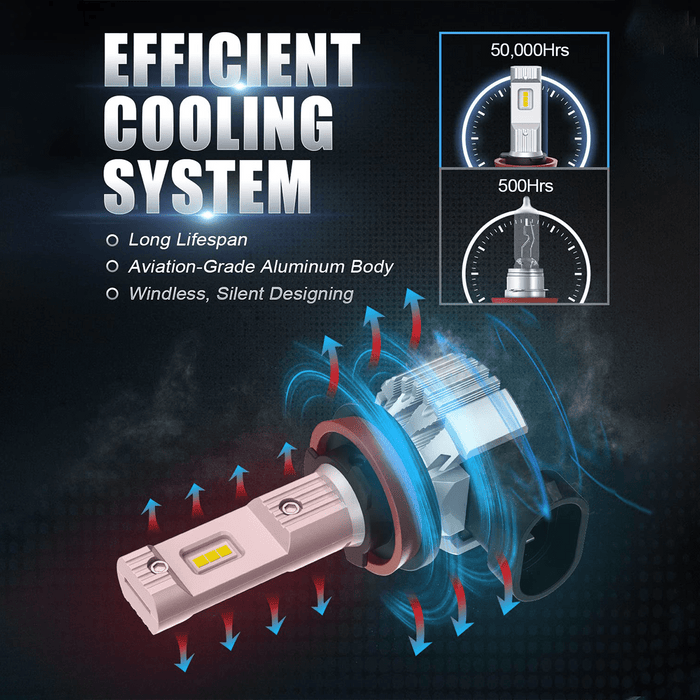
3. Active cooling solutions
To overcome the limitations of passive cooling (heatsinks), many high-performance LED headlamp bulbs incorporate active cooling systems. These systems typically involve a small fan or other cooling mechanism that actively circulates air around the heatsink, enhancing heat dissipation. By continuously removing the hot air surrounding the LED bulb, active cooling helps maintain optimal operating temperatures, ensuring consistent light output and prolonging the bulb's lifespan.
4. Benefits of active cooling
Effective active cooling in LED headlamp bulbs offers several benefits:
a. Consistent light output: By maintaining optimal operating temperatures, active cooling prevents the LED chip from overheating, which can cause a reduction in light output over time.
b. Color stability: Overheating can cause the color temperature of the LED bulb to shift, resulting in a change in the color of the light output. Active cooling helps maintain color stability by keeping the LED chip at a consistent temperature.
c. Longer lifespan: By preventing overheating, active cooling reduces the thermal stress on the LED chip and other electronic components, ultimately extending the bulb's lifespan.
d. Improved reliability: Active cooling systems help ensure that LED headlamp bulbs operate reliably in various weather conditions and temperatures, reducing the risk of unexpected failure.

5. Considerations for active cooling systems
When choosing LED headlamp bulbs with active cooling, it's essential to consider factors such as the quality of the cooling system, noise levels, and the bulb's compatibility with your vehicle's headlamp housing. High-quality active cooling systems should be efficient, durable, and relatively quiet to avoid distracting the driver.In conclusion, active cooling is crucial for LED headlamp bulbs to maintain optimal performance, color stability, and longevity. By effectively dissipating the heat generated by the LED chip and electronic components, active cooling systems ensure that LED bulbs can provide reliable, high-quality illumination in a compact package, making them an attractive choice for automotive lighting upgrades.

