As a driver, understanding the difference between high beams and low beams is crucial for safe driving and proper vehicle operation. In this article, we'll explore the key differences between high beams and low beams, and provide guidance on when to use each correctly.
What Are High Beams?
High beams, also known as bright lights or full beams, are the brightest setting on your vehicle's headlights. They are designed to illuminate a greater distance ahead of your vehicle, typically up to 350 feet. High beams are particularly useful when driving on dark, unlit roads with no oncoming traffic.
What Are Low Beams?
Low beams, also called dipped headlights, are the default setting for most vehicles' headlights. They are angled downward and provide a shorter range of illumination compared to high beams, usually around 200 feet. Low beams are designed to provide sufficient visibility without blinding oncoming drivers.
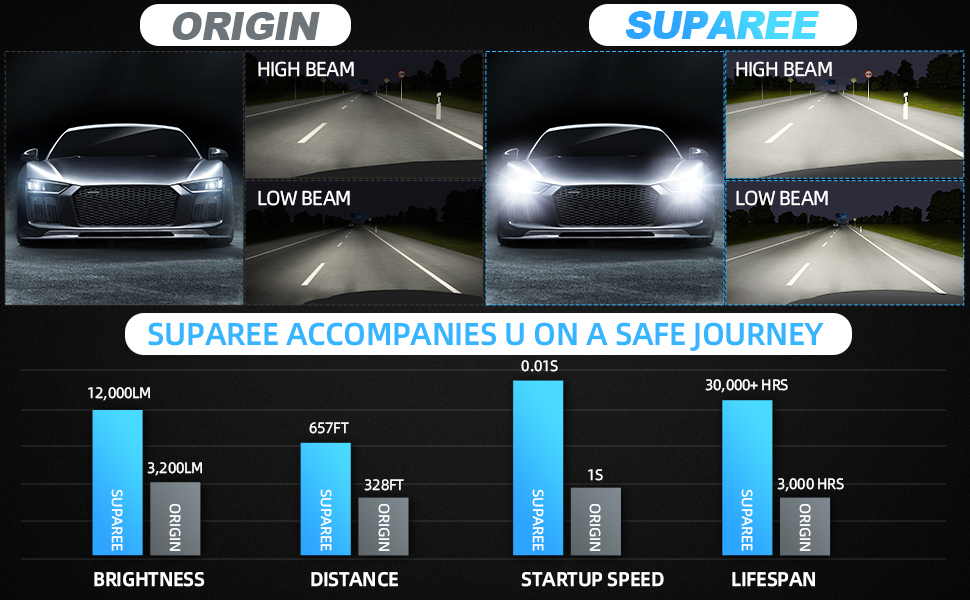
| Beam | High | Low |
| Beam Angle | Straight/Upwards | Towards the ground/road |
| Focus | Long-range | Short-range |
| Light Coverage | ~100 meters (330 ft) | ~40 meters (130 ft) |
| Best For | Dark rural areas, small roads, etc. | Nighttime driving, tunnels, etc. |
| Activation Period | Very dark areas with no oncoming traffic or cars ahead | At night, tunnels, dim areas |
| Glare | High, will blind other drivers | No |
| Activation | Manual | Automatic or Manual |
| Legal? | Yes | Yes |
| Upgrade? | Can be upgraded to LED or HID | Can be upgraded to LED or HID |
Key Differences Between High Beams and Low Beams
-
Illumination Range: High beams illuminate a greater distance ahead of the vehicle compared to low beams.
-
Beam Angle: Low beams are angled downward to avoid blinding oncoming traffic, while high beams are aimed straight ahead for maximum visibility.
-
Power Consumption: High beams typically consume more power than low beams due to their increased brightness.
When To Use High Beams
-
Dark, Unlit Roads: When driving on roads with no streetlights and no oncoming traffic, high beams can significantly improve visibility and help you spot potential hazards.
-
Rural Areas: In rural settings with minimal traffic, high beams can be used more frequently to navigate winding roads and spot animals or obstacles.
-
No Oncoming Traffic: Ensure there are no oncoming vehicles or pedestrians before switching to high beams to avoid blinding others.
When To Use Low Beams
-
Urban Areas: In well-lit urban environments, low beams provide sufficient visibility while minimizing glare for other drivers.
-
Oncoming Traffic: Always use low beams when there are oncoming vehicles to avoid blinding other drivers.
-
Foggy Conditions: Low beams are more effective in foggy conditions as they produce less glare and provide better visibility than high beams.
-
Following Other Vehicles: When following another vehicle, use low beams to avoid blinding the driver ahead of you.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between high beams and low beams, and knowing when to use each correctly, is essential for safe and responsible driving. By using high beams on dark, unlit roads with no oncoming traffic, and low beams in urban areas, foggy conditions, and when sharing the road with other vehicles, you can significantly improve your visibility and reduce the risk of accidents.

